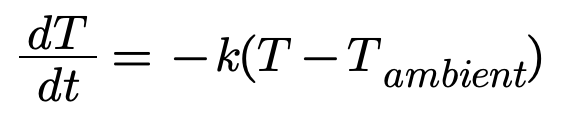1. Understanding the Problem
The goal is to model how the temperature of food changes over time based on external conditions (ambient temperature, initial food temperature, cooling/heating rates, etc.) and predict when it reaches a safe consumption temperature.
Key engineering concepts involved:
- Heat Transfer (Conduction, Convection, Radiation)
- Newton’s Law of Cooling
- Thermal Equilibrium
2. Mathematical Model:
Newton's Law of Cooling
Newton’s Law of Cooling states that the rate of change of temperature of an object is proportional to the difference between its temperature and the surrounding temperature:
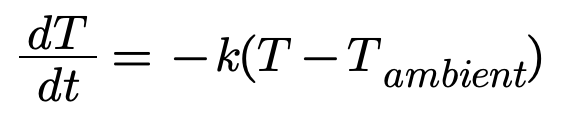
where
- dT/dt : Rate of change of temperature over time.
- k: Cooling constant (specific to the material and environment).
- T: Current temperature of the object.
- Tambient: Ambient (surrounding) temperature.
3. Implementing in Python
We can numerically solve this equation using numpy in Python and predict the time required for food to reach a safe consumption temperature while putting everything on a graph using matplotlib.
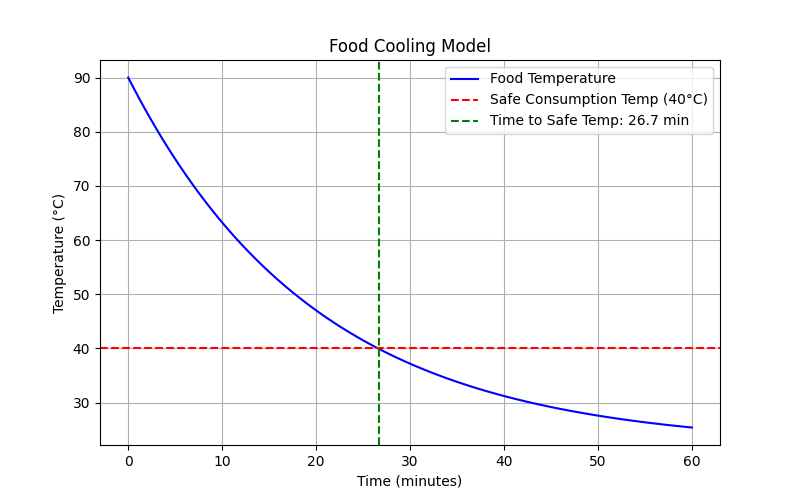
Example: Modeling Cooling of Hot Food
This graph from Python simulates food cooling from 90°C to a safe consumption temperature of 40°C at an ambient temperature of 22°C.
4. Extending the Model
- Heating Model: Adjust for heat transfer inside an oven, considering Fourier’s Law of Heat Conduction.
- Complex Shapes: Use Finite Element Analysis (FEA) for non-uniform food items.
- Real-world data integration: Implement sensor-based readings using IoT for real-time predictions.
- Machine Learning Approach: Train models on past food temperature data to predict cooling or heating times dynamically.
5. Applications
- Food Safety: Ensure perishable food doesn’t enter the “danger zone” (5°C–60°C) for bacteria growth.
- Microwave Cooking Models: Predict heating times to avoid overheating or undercooking.
- Cold Chain Logistics: Monitor and predict food temperature during transportation.